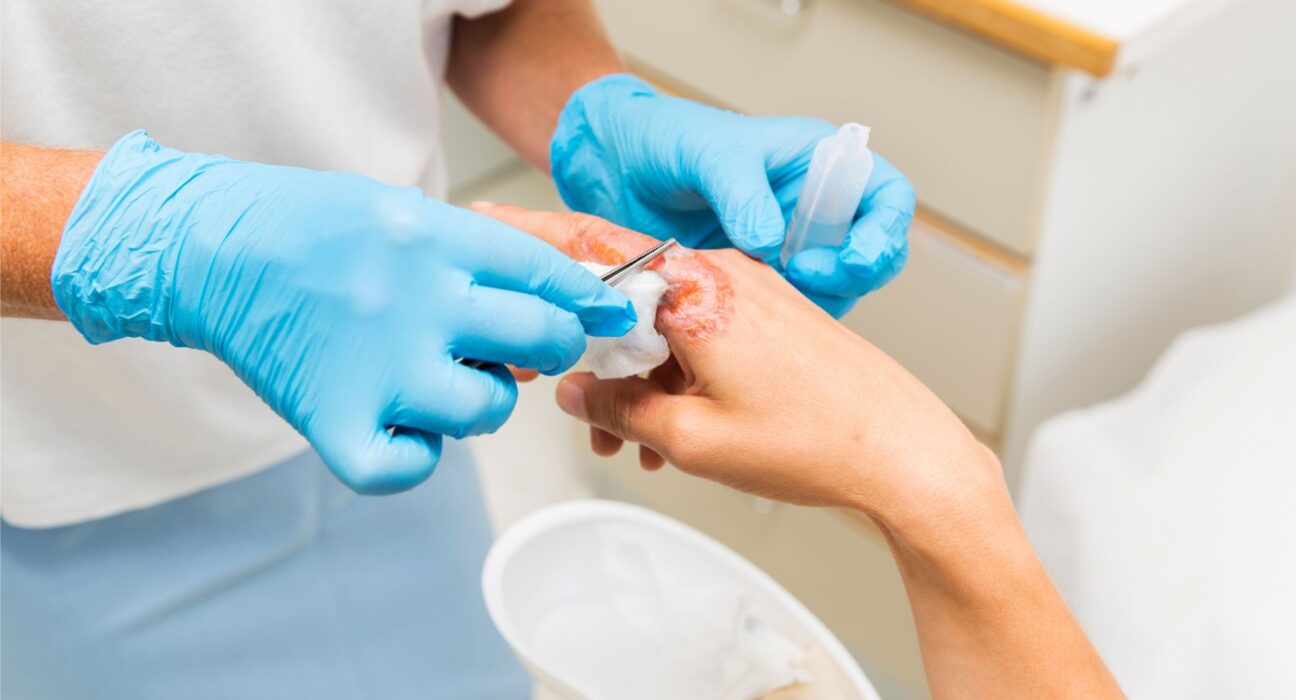
Wound care is a critical aspect of healthcare, especially for patients with chronic conditions, post-surgical wounds, or injuries that require specialized attention. A Certified Wound Specialist (CWS) is a highly trained professional who specializes in the assessment, treatment, and management of complex wounds. This certification, offered by the American Board of Wound Management (ABWM), signifies expertise in wound care and ensures that healthcare providers can deliver high-quality treatment to improve patient outcomes.
The Role of a Certified Wound Specialist
A Certified Wound Specialist is responsible for diagnosing, treating, and preventing a variety of wounds, including pressure ulcers, diabetic foot ulcers, surgical wounds, burns, and non-healing wounds. Their role includes:
- Comprehensive Wound Assessment – Evaluating the type, depth, and severity of wounds.
- Treatment Planning – Developing individualized care plans based on the patient’s medical history and wound type.
- Application of Advanced Wound Care Techniques – Using techniques such as negative pressure wound therapy, bioengineered tissue substitutes, and hyperbaric oxygen therapy.
- Infection Prevention and Management – Identifying and treating wound infections to promote faster healing.
- Patient and Caregiver Education – Teaching patients and caregivers proper wound care techniques to prevent complications.
- Collaboration with Healthcare Teams – Working alongside doctors, nurses, physical therapists, and other specialists to optimize treatment outcomes.
How to Become a Certified Wound Specialist
To become a Certified Wound Specialist, candidates must meet specific educational and professional requirements before taking the certification exam. The process includes the following steps:
1. Meet Educational and Professional Requirements
Candidates must have a background in a healthcare-related field. Eligible professionals include physicians, registered nurses, nurse practitioners, physician assistants, physical therapists, and other licensed medical professionals with relevant wound care experience.
2. Gain Clinical Experience
A minimum of three years of experience in wound care is typically required to qualify for the CWS certification. This hands-on experience ensures candidates have practical knowledge of diagnosing and treating various wound types.
3. Pass the Certification Exam
The Certified Wound Specialist (CWS) Exam, administered by ABWM, tests candidates on various aspects of wound management, including wound healing physiology, patient assessment, treatment interventions, and infection control. The exam consists of multiple-choice questions and requires a deep understanding of evidence-based wound care practices.
4. Maintain Certification
Once certified, wound specialists must renew their certification every ten years. Continuing education, attending workshops, and staying updated on advancements in wound care are essential for maintaining certification status.
Benefits of Becoming a Certified Wound Specialist
Becoming a Certified Wound Specialist offers several professional and personal benefits:
- Career Advancement – Certification enhances credibility and opens up new job opportunities in hospitals, wound care centers, home health agencies, and private practice.
- Higher Salary Potential – Wound care specialists often earn higher salaries compared to non-certified healthcare professionals in similar roles.
- Improved Patient Outcomes – Advanced training allows specialists to provide superior care, leading to better healing rates and reduced complications.
- Professional Recognition – A CWS certification is a mark of excellence that distinguishes professionals in the competitive healthcare field.
- Increased Knowledge and Expertise – Certification ensures that professionals are up-to-date with the latest wound care treatments, technologies, and best practices.
Where Do Certified Wound Specialists Work?
Certified Wound Specialists can work in various healthcare settings, including:
- Hospitals – Treating inpatients with post-surgical wounds, pressure ulcers, and trauma-related wounds.
- Outpatient Wound Care Clinics – Providing specialized wound management for patients with chronic or non-healing wounds.
- Home Healthcare – Assisting patients with wound care in their own homes, particularly those with mobility challenges.
- Skilled Nursing Facilities – Managing wound care for elderly or long-term care patients.
- Private Practice – Offering wound care services independently or as part of a multidisciplinary healthcare team.
The Future of Wound Care and the Role of Certified Specialists
As the healthcare industry continues to evolve, the demand for wound care specialists is expected to grow. The increasing prevalence of diabetes, obesity, and aging populations contributes to a higher incidence of chronic wounds, making specialized care more essential than ever. Advances in biotechnology, telemedicine, and regenerative medicine are also shaping the future of wound care, creating more opportunities for Certified Wound Specialists to apply cutting-edge treatments.
Conclusion
A Certified Wound Specialist (CWS) plays a crucial role in modern healthcare by providing expert care for acute and chronic wounds. Earning this certification not only enhances a professional’s credentials but also ensures that patients receive the best possible treatment to promote faster healing and prevent complications. As the field of wound care continues to expand, the need for highly trained specialists will remain strong, making this certification a valuable asset for healthcare professionals committed to excellence in patient care.