Introduction
The Skin Replacements and Substitutes Market represents a dynamic segment within the healthcare industry, gaining momentum due to rising demand for advanced wound healing and reconstructive solutions. These products are engineered to replace or regenerate damaged or lost skin tissue and cater to a broad spectrum of medical needs, from chronic wounds and burns to cosmetic surgeries and congenital skin disorders. As medical science continues to evolve, the role of biologically engineered skin substitutes and synthetic alternatives is expanding rapidly. Increasing global awareness, technological innovations, and growing patient expectations are driving interest in this vital area of regenerative medicine.
Skin substitutes range from temporary coverings to full-thickness constructs designed to simulate or restore native skin’s biological functions. These technologies can be derived from living cells, biomaterials, or a combination of both, and often integrate anti-inflammatory agents, scaffolds, or stem cells. With healthcare systems prioritizing improved patient outcomes and lower recovery times, skin replacement therapies have become an essential resource in both acute and chronic wound management. Ongoing developments in biomaterials and biofabrication continue to shape the next generation of regenerative skin products.
The Evolution
Skin repair has evolved from basic wound dressing to sophisticated tissue engineering over centuries. Ancient practices involved plant-based applications and rudimentary grafting techniques. With limited understanding of skin biology, early practitioners could only provide temporary relief. By the 19th century, autografting—using the patient’s own tissue—became more common, particularly for severe burns.
The development of allografts (donor skin) and xenografts (animal-derived skin) expanded therapeutic possibilities. Mid-20th century saw the refinement of surgical techniques for skin transplantation, along with improved sterility and grafting protocols. However, it was the emergence of synthetic materials and cell culture technologies in the 1980s that heralded a new era. Products such as Integra and AlloDerm introduced scaffold-based solutions capable of supporting cellular regrowth and vascularization.
As understanding of tissue mechanics and immunology improved, bioengineered substitutes incorporating living cells and bioactive compounds emerged. The integration of nanotechnology, 3D bioprinting, and stem cell research redefined treatment parameters. Regenerative strategies now include decellularized skin matrices designed to promote host integration and vascularization, with researchers pushing the limits of full-thickness skin mimicry.
Today, the market encompasses a diverse array of skin substitutes ranging from basic wound covers to complex constructs capable of restoring sensory and protective functions. The convergence of cell science, material engineering, and clinical expertise drives continuous innovation and product refinement.
Read More: https://www.databridgemarketresearch.com/reports/global-skin-replacements-and-substitutes-market
Market Trends
The Skin Replacements and Substitutes Market is influenced by several transformative trends that are shaping its future:
- Advanced biomaterials, including collagen, elastin, and glycosaminoglycans, are being tailored to mimic skin’s mechanical and biochemical properties, improving healing and compatibility.
- Bioprinting technologies enable the layer-by-layer fabrication of skin structures with precise control over cellular architecture. This facilitates the creation of patient-specific substitutes using imaging and diagnostic inputs.
- Regenerative therapies using induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) and mesenchymal stem cells offer reduced risk of rejection and enhanced regenerative capacity, making them increasingly attractive for chronic wound care.
- Digital health tools are being integrated into skin treatment protocols. Wound monitoring devices and AI-powered diagnostic platforms support remote care and track healing progress, boosting adherence and early intervention.
- Cosmetic dermatology continues to influence the market, with skin substitutes being used in post-laser treatments, scar revision, and reconstructive surgeries, adding an aesthetic dimension to traditional therapeutic applications.
- Miniaturized and wearable delivery devices are being developed for targeted application of skin substitutes. These facilitate on-the-go wound care and empower patients with better autonomy.
- Environmental sustainability is gaining attention. Manufacturers are evaluating biodegradable substitutes and eco-friendly packaging to address ecological concerns.
- Value-based healthcare models are influencing procurement decisions. Products with proven cost-effectiveness and measurable patient outcomes are gaining traction over experimental or high-cost solutions.
These trends collectively reinforce the market’s alignment with precision medicine, sustainability, and patient-centric care.
Challenges
While the market is growing robustly, several challenges continue to test its potential and scalability:
- Cost remains a major barrier. Biologic substitutes often require complex manufacturing, cryopreservation, and specialized handling, making them inaccessible for low-income settings.
- Regulatory pathways are inconsistent across regions. Products may be classified as medical devices, biologics, or tissue-engineered therapies, requiring multi-tiered approval processes that delay commercialization.
- Immune response to non-autologous materials remains a concern. Substitutes derived from donor tissues or animals can trigger rejection or inflammation, compromising healing outcomes.
- Achieving full skin functionality—such as sweat production, pigmentation, and tactile sensation—is still an unresolved challenge. Many substitutes offer structural repair but fall short of physiological restoration.
- Limited long-term data impairs confidence in newer technologies. Post-marketing surveillance and real-world evidence gathering need improvement to support broader adoption.
- Supply chain disruptions affect product availability. Dependence on live tissue sourcing, cold-chain logistics, and regional regulations complicates distribution strategies.
- Ethical considerations around stem cell sourcing, donor tissue procurement, and biofabrication practices continue to demand scrutiny and stakeholder transparency.
- Clinical education gaps persist. Successful use of skin substitutes requires trained wound care specialists and interprofessional collaboration, which are unevenly distributed globally.
Addressing these challenges requires coordinated effort among regulators, researchers, industry leaders, and healthcare providers.
Market Scope
The market spans a broad spectrum of clinical and commercial dimensions. Applications include trauma and burn care, chronic wound healing, aesthetic and cosmetic procedures, and pediatric skin conditions. Skin substitutes are used in hospital surgical suites, outpatient clinics, ambulatory care centers, and increasingly in home-based care.
The market includes several product categories:
- Biologic products such as autografts, allografts, xenografts, and decellularized matrices.
- Synthetic substitutes made from polymers, silicone, and hydrogel composites.
- Hybrid technologies that combine biomaterials with cellular components for improved regeneration.
Form factors vary widely and include films, sprays, matrices, patches, and gels. Each is designed with specific use cases and healing goals in mind. While burn treatment remains the primary driver, chronic wound management (especially diabetic and venous ulcers) is rapidly overtaking other indications in terms of volume and cost impact.
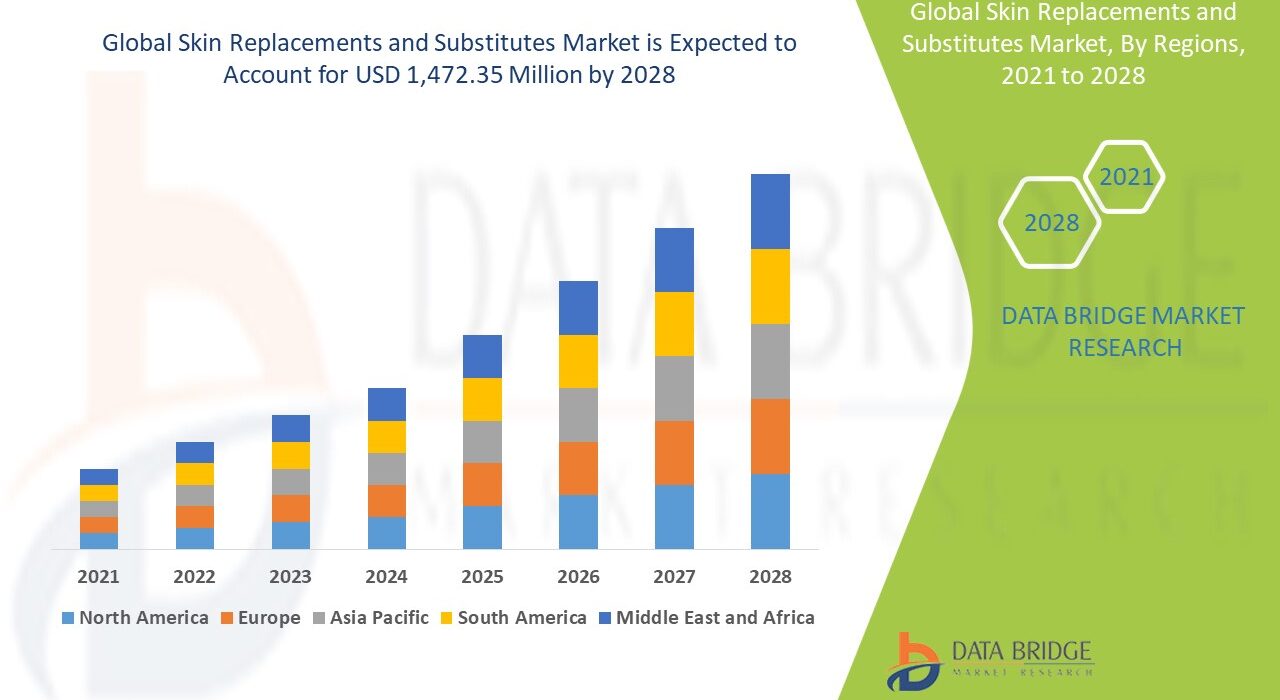
Geographic adoption varies. North America and Europe lead due to strong healthcare infrastructure and reimbursement policies. Asia-Pacific is emerging as a high-growth region, propelled by aging demographics and increased incidence of diabetes. Latin America and Middle East markets are expanding steadily, fueled by government initiatives and rising urban trauma cases.
Factors Driving Growth
Multiple intersecting drivers are fueling expansion across the global Skin Replacements and Substitutes Market:
- Demographic shifts, especially population aging, are increasing the prevalence of age-related skin complications and slow-healing wounds.
- Rising chronic disease burden, particularly diabetes and peripheral vascular disorders, is creating sustained demand for effective skin therapies.
- Improved healthcare access and awareness in emerging economies are opening new markets for skin replacement products.
- Technological integration into wound care workflows—from diagnosis to follow-up—is optimizing treatment timelines and reducing hospital stays.
- Research collaboration between academia and industry is accelerating product discovery, testing, and deployment.
- Government funding initiatives and favorable policy frameworks are encouraging innovation in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
- Global health crises, such as natural disasters and conflict zones, have highlighted the urgency for portable, rapid-deployment skin repair solutions.
- Growing acceptance of biologics and cell therapies is reducing stigma and increasing patient willingness to explore advanced options.
- Clinical guidelines are evolving to include skin substitutes as first-line treatments for chronic wounds, further legitimizing their usage.
- Public-private partnerships are enabling large-scale pilot programs, especially for underserved populations and veteran care programs.
These growth factors position the market for long-term sustainability and broad-based clinical integration.
Conclusion
The Skin Replacements and Substitutes Market is undergoing profound transformation, becoming one of the most promising domains in regenerative medicine. By blending biological insight with material science, today’s skin substitutes offer far more than passive protection—they actively promote healing, reduce inflammation, and facilitate tissue regeneration.
Despite inherent complexities in regulation, cost, and scalability, the momentum of innovation is driving superior clinical outcomes and expanding access. The convergence of aesthetic medicine, chronic wound management, and trauma care under one therapeutic umbrella demonstrates the versatility and necessity of skin replacement solutions.
Market evolution will be shaped by how stakeholders respond to emerging trends, refine technologies, and overcome access barriers. Continued investment, research, and education will ensure that skin substitutes are not just futuristic concepts, but mainstream tools that reshape how we heal the human body. Ultimately, the ability to restore skin—and all the life it covers—is a powerful symbol of medical progress and the enduring pursuit of human wellbeing.